Tretinoin is a particularly well-known prescription retinoid for the treatment of skin ageing and acne, but it’s not the only one. There’s also retinol, retinaldehyde and adapalene to name a few.
If you’re confused about how to choose a retinoid treatment and where to start, we’re here to help. In this post, we’ll explain what retinoids are, the differences between tretinoin and retinol, and ways to choose the correct one for your skin type and skin goals.
What are retinoids?
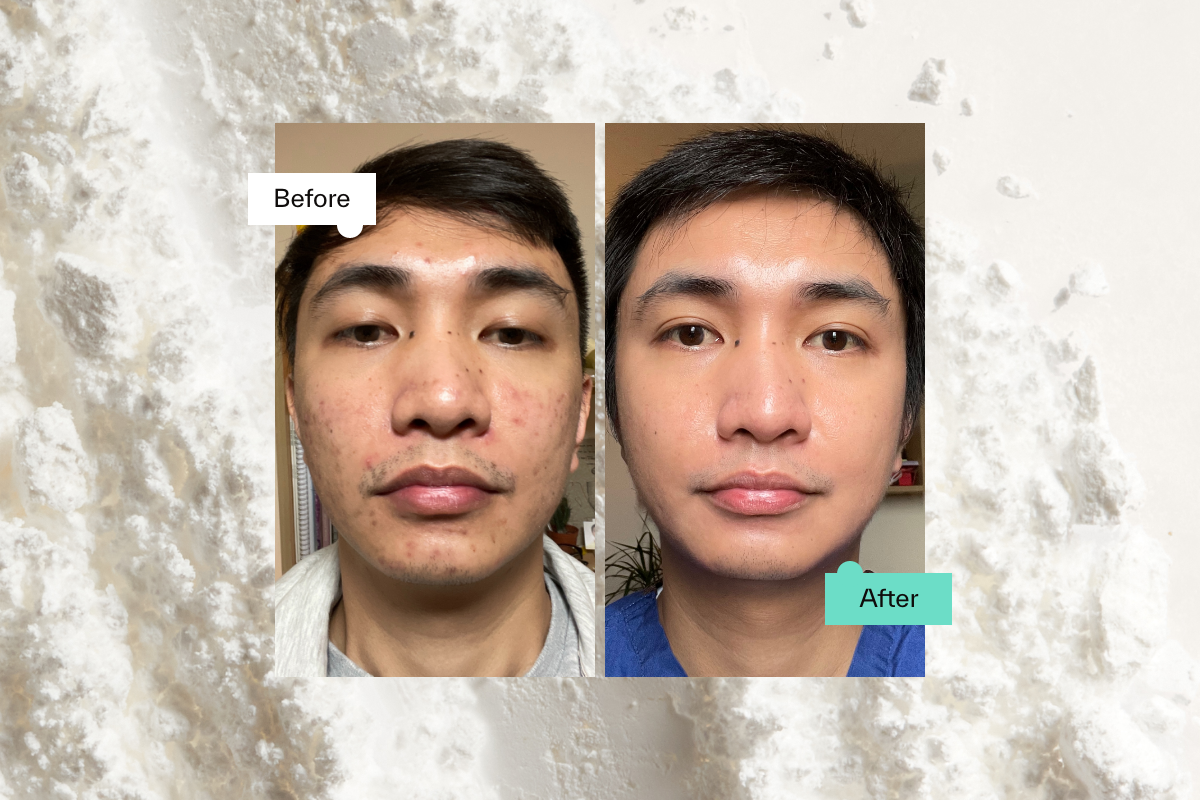
Derived from Vitamin A, retinoids are active skincare ingredients that play a crucial role in promoting healthy skin. When applied regularly, they work by promoting facial skin cell turnover, which in turn prevents your pores from clogging, boosts collagen synthesis and collagen production, and encourages the growth of new skin cells. (1) The result of long-term use is smoother, clearer and firmer – in as little as 8 weeks when using prescription retinoids like tretinoin.
Tretinoin
Tretinoin is an active ingredient that’s only available on prescription. It’s also considered a gold standard dermatological treatment, and it’s one of the most talked-about ingredients in skincare. When you apply tretinoin cream, it can directly bind to retinoic acid receptors in the skin, which means it doesn’t have to go through conversion processes to become active. Tretinoin can therefore get to work on your facial skin immediately, making it more potent than retinol or retinaldehyde.
Studies show tretinoin cream is one of the most potent and effective retinoids – hence its gold standard status. It works on both the surface levels and deeper levels of your skin. It helps promote healthy skin by increasing skin cell turnover – removing old dead skin cells, and replacing them with fresh new ones. This makes tretinoin a versatile acne treatment, as well as an effective treatment for premature skin ageing, hyperpigmentation (uneven skin tone), photodamaged skin, rough skin texture, UV damage, overall skin glow, or a combination of these skin conditions. (2)
When can I expect to see results?
With tretinoin, patience and consistency is key. Since topical tretinoin cream is a powerful active ingredient, you may experience some side effects when you start, but these should subside after a week or two. Improvements to your skin concerns from the effects of tretinoin are often noticeable after around two to four weeks of regular use. And although it can take up to four months to see visible results – the benefits of long-term use are worth it.
Retinol And Retinaldehyde Benefits
Topical retinoids don’t just vary in name and type, they also come in a variety of strengths.
The difference between retinol formulations and tretinoin is that retinol is a less potent member of the retinoid family. Unlike prescription retinoids, retinol has to go through conversions in the facial skin to turn into the active form called retinoic acid. Retinol is available without a prescription, and is used in many cosmetic products and over-the-counter skincare products. The effects of retinol are similar to tretinoin, but the key difference is that they’re up to 20x less potent than their prescription counterparts.
Like tretinoin, retinol and retinaldehyde are active ingredients that are also backed by science to help treat photodamaged skin. These topical treatments also boost the rate of cell turnover, collagen production, the treatment of acne, uneven skin tone and overall skin glow for healthy skin. You may choose to start with cosmetic products that contain retinol or retinaldehyde if you’re new to retinoids, or have reactive or sensitive skin. It may just take longer to see results, as the efficacy of retinol is lower than that of tretinoin. (3)
Is Tretinoin The Same As Retinol?
While tretinoin and retinol are both members of a powerful group of Vitamin A derivatives, they are not the same.
Tretinoin, also known as retinoic acid, is a prescription-strength retinoid that directly binds to retinoic acid receptors in the facial skin, stimulating cell turnover and collagen production. It is highly potent and effective in treating various skin concerns such as acne, fine lines, photoaged skin and hyperpigmentation.
On the other hand, retinol is a milder over-the-counter form of vitamin A that needs to undergo conversion in the facial skin before becoming active. It is typically gentler and better tolerated by sensitive skin compared to tretinoin but may take longer to produce noticeable results. Dermatica would emphasise that while both tretinoin and retinol offer beneficial effects for healthy skin, their potency and mechanisms of action differ, making them suitable for different individuals and skin concerns.
Is It Better To Use Tretinoin Or Retinol?
Tretinoin, a prescription-strength retinoid, is typically more potent and effective in addressing concerns like acne, fine lines, photodamaged skin, photoaged skin and dark spots. Its molecular structure allows it to directly bind to retinoic acid receptors in the skin, promoting rapid cell turnover and collagen production. However, it can also cause more irritation and sensitivity, especially when you first start using it.
On the other hand, retinol, an over-the-counter derivative of vitamin A, is milder and generally better tolerated by easily-irritated skin or sensitive skin. While it may take longer to see beneficial effects compared to tretinoin, retinol can still provide noticeable improvements in photoaged skin, skin texture, tone, and overall appearance.
The choice between tretinoin and retinol depends on individual skin concerns, sensitivity levels, and preferences. We recommend starting a consultation with us, or visiting your dermatologist, for personalised advice and treatment plans.
Can I Use Tretinoin And Retinol Together?
Our dermatology experts strongly advise you to avoid using tretinoin and retinol at the same time. Both topical retinoids are potent forms of vitamin A derivatives that promote skin cell turnover and collagen production. Therefore, with long-term use, both can lead to significant anti-ageing effects in skin texture, skin roughness and the appearance of photoaged skin. However, the combination of retinol with topical tretinoin can also expose your skin to potential side effects like skin irritation, redness, retinisation, and sensitivity. These irritant effects could overwhelm your skin’s tolerance threshold – cancelling out any beneficial effects. (4)
Some individuals might be able to handle the combination of topical tretinoin and retinol without potential side effects. However, your tretinoin prescription should already be personalised with the correct concentration to suit your skin type and tolerance levels. Therefore adding a retinol to your routine as well may overload your skin’s tolerance, cause adverse effects like excessive exfoliation – and potentially damage your skin barrier.
If you’re still unsure, reach out to our dermatology team from your dashboard if you’re a subscriber. Our experts are always on hand to help. Or get medical advice from a dermatologist or skincare professional in-person to make sure you’re using the most suitable products based on your skin type, skin sensitivity levels, and skin goals.
Retinoids, Retinol and Light Sensitivity
Tretinoin and retinol are both sensitive to light. Exposure to light, especially sunlight, can affect the stability of retinol and tretinoin, causing it to degrade and lose its effectiveness over time. To maintain the potency of products that contain retinoids, it’s important to store them in opaque or dark containers and keep them away from direct sunlight. (5)
Use your prescription retinoid or retinol products during your nighttime routine to help minimise the risk of your product degrading from sunlight, and ensure it is working to its full potential.
What To Do If You Experience Retinisation
When you first start using a retinoid product, such as one containing tretinoin or retinol, it’s very normal to experience the following common side effects.
Skin Irritation
Both retinol and tretinoin can cause skin irritation, like redness, dryness, flakiness and peeling. Especially during the first few weeks. These adverse effects are often referred to as retinisation and are normal. It means your skin is adjusting to your new treatment. If you’re lucky and don’t experience any side effects, your treatment is still working. To treat these areas, use Restoring Ceramide Skin Balm as your final skincare step before bed to protect and nourish flaky skin.
Increased UV Sensitivity
Vitamin A derivatives like tretinoin cream and retinol also make your skin more sensitive to sunlight, which can increase the risk of sunburn, irritation, photoaged skin and UV damage. Exposure to UV radiation while using retinoids can also counteract its benefits and potentially reverse your progress, or worsen skin issues like melasma or hyperpigmentation.
It’s therefore so important to use sunscreen daily when using retinol products, even on cloudy days, indoors or during the winter months. Look for a broad-spectrum sunscreen like SPF50 Photodamage Defence Sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Apply it generously to all exposed skin areas. Additionally, wear protective clothing, seek shade, and avoid prolonged sun exposure to help minimise the risk of adverse effects while using retinoids. (5)
Stinging Or Burning Sensations
You may experience stinging or burning when you apply retinol or tretinoin – particularly if you have sensitive skin. This should feel like a mild tingle and subside quickly. If the adverse effects persist, stop using your product and check in with a dermatology expert from Dermatica or your dermatologist for medical advice.
Dry Skin
Tretinoin and conventional formulations of retinol can cause temporary dryness and dehydration, leading to some tightness or mild discomfort. Moisturise regularly with a ceramide-rich, non-comedogenic moisturiser like the Nourishing Ceramide + Peptide Moisturiser.
Acne Breakouts
In the initial weeks of using a topical retinoid like tretinoin or retinol, you may notice a temporary worsening of acne symptoms. We often refer to this as the “purging” stage. Be sure to only use gentle, fragrance free, non-comedogenic skincare that’s designed to enhance the beneficial effects of active ingredients. Like the science-backed skincare products from our daily essentials range.
How Our Dermatology Experts Make The Right Choice For Your Skin
With so many options available, it can be confusing to know which retinol formulations to choose. First and foremost you should consider your skin type, tolerance to ingredients, concerns and goals.
That’s why we always recommend a personalised approach. To find out which ingredient is right for your skin, our dermatology experts analyse the results from your free online consultation and photos. They then design a personalised formula and monthly treatment plan, at the precise strength to suit your skin type. Not only are our experts available to answer any questions you have, they also check in with you throughout your journey, and change and adapt your formula at no extra charge to optimise your results.
Check Which Retinoid Is Right For Your Skin
Ready to discover which active ingredients our dermatology experts recommend for you? Find out what formulas are suitable for your skin by visiting our website.
References
1) Zasada M, Budzisz E. Retinoids: active molecules influencing skin structure formation in cosmetic and dermatological treatments. Advances in Dermatology and Allergology [Internet]. 2019;36(4):392–7. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6791161/
2) Yoham AL, Casadesus D. Tretinoin [Internet]. PubMed. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557478/
3) Farris P. SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE: Retinol: The Ideal Retinoid for Cosmetic Solutions. Journal of drugs in dermatology: JDD [Internet]. 2022 Jul 1;21(7):s4–10. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35816071/
4) Mukherjee S, Date A, Patravale V, Korting HC, Roeder A, Weindl G. Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical interventions in aging [Internet]. 2006;1(4):327–48. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2699641/
5) Rosso JD, Harper J, Pillai R, Moore R. Tretinoin photostability: comparison of micronized tretinoin gel 0.05% and tretinoin gel 0.025% following exposure to fluorescent and solar light. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2024 Jan 18];6(2):25–8. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3579485/
Ash Sharma
Dr Ashwin Sharma is a medical doctor and writer with a particular interest in health technology, artificial intelligence and medical weight loss. He completed his training at the University of Leicester and Imperial College London, and has since been exploring the intersections of medicine, technology, and communication.