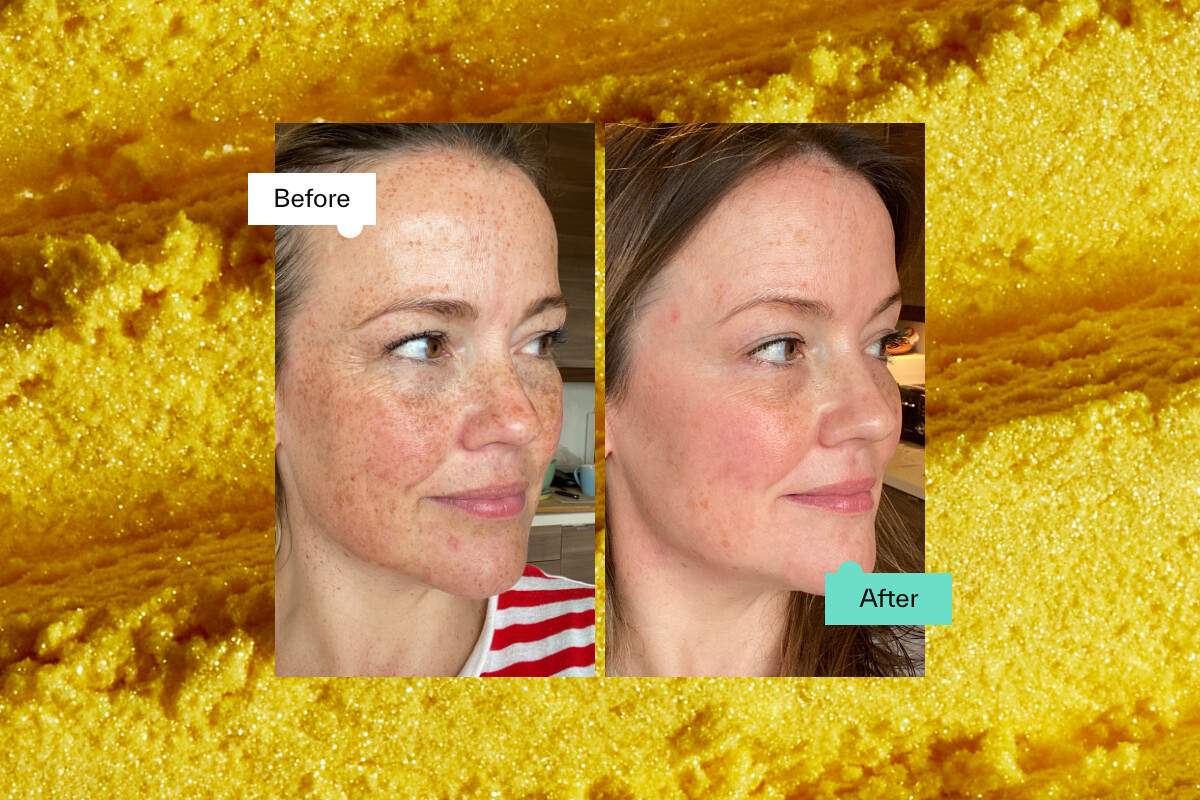
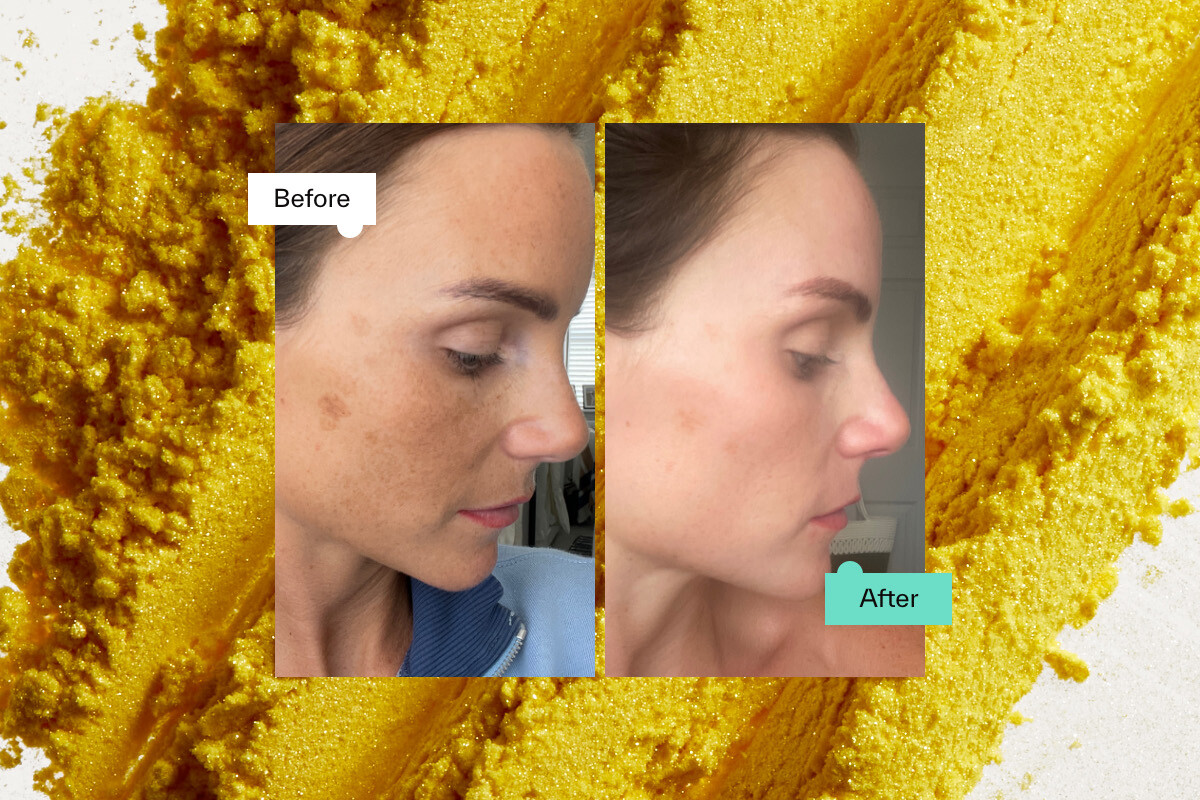
With so many products promising youthful, radiant skin, it would take months of research to decide which one works, or is “the best.” Especially because the way we age varies enormously from person to person depending on our genetics, lifestyle, skin type, how consistent our skincare routine is and our overall health.
To navigate the neverending flurry of age-defying serums and creams, we’ve compiled FAQs from consultations and our Facebook Community. We’ll cover everything you want to know, so you can choose the best anti-ageing cream for your skin.
Which cream is best for ageing skin?
Of all our organs, signs of ageing are the most visible on our skin. If you want to slow down the signs of skin ageing, the best skincare to choose will depend on your skin type, skin concerns, intolerances and allergies (if any), and textural preferences.
Rather than recommending a specific product, we suggest turning your attention more to ingredient lists. For example, products that contain gold standard key ingredients like retinoids, antioxidants, and peptides. These will suit most skin types, and are recommended by dermatologists to address one of the most common causes of ageing skin, known as photoageing – when exposure to sunlight prematurely damages the skin. (1)
Retinoids, also known as retinoic acid, are up to 20x more powerful than ordinary retinol and over-the-counter anti-ageing creams, so to access them you will need a licensed dermatology professional (or a board-certified dermatologist if you live in the US). They will personalise a skincare formula that suits your skin. If you can’t see a dermatologist in-person, start a consultation with Dermatica and our experts can tailor a retinoid formula and treatment plan to suit your skin goals. (2)
What is the number one anti-ageing product?
Retinoids and retinol, which are a form of Vitamin A, are considered to be among the most effective key ingredients for combating signs of ageing. They boost collagen production and reduce the signs of UV-induced early skin ageing, like fine lines, loss of elasticity and pigmentation. (3)
Studies show that antioxidants Vitamin C and Vitamin E protect the skin from environmental damage, fade dark spots and improve its overall radiance. They have a small molecular weight which allows them to penetrate deep in the skin. What’s more, the antioxidative protection is even higher when these two vitamins are combined (like in our Vitamin C 15%: Fresh Batch Ascorbic Acid) vs. when they’re formulated on their own. (4)
How do I choose an anti-ageing product that’s right for me?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all response to what the number one, must-have anti-ageing product is. Not least because the signs of ageing that concern one person may be perfectly acceptable for another. How suitable certain ingredients are will vary from person to person, too.
Whatever your skin type is, retinoids and Vitamin C are the most well-researched key ingredients to address multiple signs of ageing. It’s why they’re considered the gold standard by dermatologists.
Both retinoids and Vitamin C help stimulate collagen production, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, smooth uneven texture and even out discoloration and hyperpigmentation (e.g. melasma, uneven skin tone, sun damage, dark spots or acne scars).
When applied consistently as a night cream, most patients see results from retinoids in as little as 6 weeks. And when you add Vitamin C 15%: Fresh Batch Ascorbic Acid and SPF50 Photodamage Defence Sunscreen in the morning, you’ll also protect your skin from UV and free radical damage from pollution – the leading causes of premature skin ageing.
Do anti-ageing creams really work?
Yes, many do. Defining whether anti-ageing creams and products “work,” means seeing if they’re science-backed to slow the rate of photoageing in the skin. These products are made up of two main components: antioxidants and cell regulators.
Antioxidants such as vitamins and polyphenols slow down collagen depletion. Cell regulators like retinoids and peptides directly affect collagen – helping to speed up its production.
And when applied together, studies have shown they improve the appearance of ageing skin. (4)
Some products, however, do not. Many creams on the market make grandiose anti-ageing claims without delivering results. That’s why it’s so important to check that the ingredients and formulation are backed by science before you part with your cash.
No matter which anti-ageing day or night cream you choose, you won’t see the benefits if you don’t protect your skin with a broad-spectrum sunscreen like SPF50 Photodamage Defence Sunscreen every day. Repeated UV exposure can damage the DNA in your skin cells and cause fine lines, wrinkles, skin thickening and hyperpigmentation. Whether it’s sunny, rainy or cloudy outside, UV rays are responsible for up to 90% of photoageing and skin cancer. (5)
Is there really a product that gets rid of wrinkles?
While no topical product (applied to the skin) can eradicate wrinkles, active ingredients like retinoids and Vitamin C help reduce their appearance. Both ingredients are considered by dermatologists to be gold standard treatments for photoageing.
Retinoids boost healthy cell turnover, helping your skin renew itself and removing dead skin cells for a brighter complexion. Vitamin C also scavenges and neutralises free radicals, to protect you from the UV-induced damage that speeds up the skin ageing process. (6)
Ceramides and peptides are present in creams and moisturisers for all skin types. They soothe and protect your skin barrier, soften dry skin, slow the formation of wrinkles and support your skin’s ability to repair itself. (7)
Does your skin type affect which anti-ageing cream you should use?
Absolutely. Different skin types have different needs and reactions to certain ingredients can vary.
For example, those with combination skin or oily skin usually benefit from a lightweight cream with a non-comedogenic formula (doesn’t clog pores). If you have sensitive skin, many products made for oily or acne-prone skin can be harsh or stripping on the skin. If this applies to you, look for products that are formulated according to the NICE guidelines for sensitive skin like our Balancing Glycerin Gel Cleanser and Soothing Centella Gel Moisturiser.
Those with balanced skin, dry skin or mature skin may need richer, more moisturising cleansers and night creams with ingredients like squalane and shea butter. If you have sensitive skin, you may want to avoid products with added fragrance – and opt for evidence-based formulations like Caring Squalane Cream Cleanser and Nourishing Ceramide + Peptide Moisturiser.
Any skin type can become dehydrated (lack water), which can make our complexion appear dull. To combat this, apply Hydrating Hyaluronic Acid + Vit B5 Serum morning and evening before your moisturiser to prevent TEWL (water loss from the skin) and improve your skin health overall.
The products and ingredients you need
– Broad-spectrum sunscreen: We can’t stress how important broad-spectrum sunscreen is. It protects you from harmful UV rays, which can accelerate skin ageing, pigmentation and cause skin cancer.
– Retinoids: These Vitamin A derivatives are known for their ability to stimulate collagen production, firm skin, improve skin elasticity, refine skin tone, tackle stubborn hyperpigmentation below the surface and improve uneven skin texture.
– Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant, Vitamin C helps brighten dull skin, fade dark spots, maximise your sunscreen’s UV protection and shield against environmental stressors like pollution. Ascorbic acid is the most research-backed and powerful form of Vitamin C, but it’s also volatile – so make sure your product is packaged in an airtight, opaque bottle. (8)
– Acids and Other Active Ingredients: Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), tranexamic acid and kojic acid are all key ingredients for improving skin tone, refining skin texture and brightening dullness. (9)
Note: Avoid acids and other strong active ingredients if you’re starting retinoids for the first time. Once your skin tolerates retinoids well, you can slowly add these back into your routine to avoid skin irritation.
– Peptides: These short chains of amino acids are the building blocks of proteins that are needed by the skin, like collagen and elastin. They prevent the appearance of lines and support a firmer, younger-looking complexion. (10)
– Moisturisers: Hydrating ingredients like glycerin, ceramides, hyaluronic acid and shea butter (only use it if you have balanced/dry skin) help maintain your skin’s moisture and hydration levels. This in turn improves skin elasticity and slows down how quickly deep wrinkles form.
When you should start using a wrinkle cream
It’s never too early to start adding anti-ageing products into your skincare routine, as prevention is key. However, most dermatologists recommend starting in your mid to late twenties when the first signs of skin ageing begin to appear.
How to choose an anti-ageing cream
– Don’t get hung up on price: Expensive doesn’t always mean better. Focus on the ingredients and formulation rather than the price tag.
– Keep your skin type in mind: Choose products formulated for your skin type, whether it’s oily, dry, sensitive, or combination. For example, retinoids aren’t usually suitable for people with rosacea – as their sensitive skin won’t tolerate the ingredient well.
– Prioritise gold standard ingredients: Ingredients are gold standard when they’ve been thoroughly tested with successful outcomes.
– Be consistent: There’s no silver bullet – the more regularly you look after your skin, the better it will look for longer. Like we always say, healthy skin is a marathon not a sprint.
– Remember, you can’t reverse wrinkles: Anti-wrinkle creams will never give you the same results as a cosmetic peel or injection. They can reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles – but only procedures like Botox® or fillers will completely smooth their appearance (albeit temporarily).
The more you understand your skin, the better your choice of anti-ageing cream or moisturiser will be, as the ingredients will target your specific needs. Already a Dermatica customer? Check you’re making the right choice by reaching out to our expert team at any time from your dashboard.
If you need help from trusted dermatology experts, start a consultation with Dermatica today. Our team assesses your photos and concerns entirely online, then tailors a bespoke treatment plan and personalised formula to target your goals.
Remember to prioritise ingredients like retinoids, antioxidants, and sunscreen, and tailor your skincare routine to suit you. Doing this will prolong a healthy, younger-looking complexion and prevent skin ageing from sun exposure, pollution and free radicals.
References
1) Knaggs H, Lephart ED. Enhancing Skin Anti-Aging through Healthy Lifestyle Factors. Cosmetics [Internet]. 2023 Oct 1;10(5):142. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/10/5/142
2) Ganceviciene R, Liakou AI, Theodoridis A, Makrantonaki E, Zouboulis CC. Skin anti-aging strategies. Dermato-Endocrinology [Internet]. 2012 Jul 1;4(3):308–19. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3583892/
3) Smith, J., & Johnson, A. (2019). Retinoids in the treatment of skin ageing: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 14, 325–332. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S188003
4) Rattanawiwatpong P, Wanitphakdeedecha R, Bumrungpert A, Maiprasert M. Anti‐aging and brightening effects of a topical treatment containing vitamin C, vitamin E, and raspberry leaf cell culture extract: A split‐face, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 2020 Jan 24;19(3):671–6.
5) Hooper D, Tedaldi R, Iglesia S, Young MB, Kononov T, Zahr AS. Antioxidant Skincare Treatment for Hyperpigmented and Photodamaged Skin: Multi-Center, Open-Label, Cross-Seasonal Case Study. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2024 Apr 10];16(10):31–8. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10617894/
6) Guan LL, Lim HW, Mohammad TF. Sunscreens and Photoaging: A Review of Current Literature. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2021 Aug 13;22(6):819–28.
7) Hanene Bzioueche, Tamelghaghet M, Bérengère Chignon-Sicard, Bazile N, Hauchecorne P, Maria Barbero Calderón, et al. Ceramide ADTM Restores Skin Integrity and Function following Exposure to House Dust Mite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences [Internet]. 2023 May 25 [cited 2024 Feb 21];24(11):9234–4. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10252232/
8) Jaros-Sajda A, Budzisz E, Erkiert-Polguj A. Ascorbic Acid Treatments as Effective and Safe Anti-Aging Therapies for Sensitive Skin. Antioxidants. 2024 Jan 30;13(2):174–4.
9) Gomes, A. J. P. C., Lunardi, C. N., Gonzalez, S., Tedesco, A. C., & De Oliveira, D. P. (2019). Kojic acid in hyperpigmented skin: a systematic review. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 31(5), 522–527. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2019.1619001
10) He B, Wang F, Qu L. Role of peptide–cell surface interactions in cosmetic peptide application. Frontiers in pharmacology [Internet]. 2023 Nov 13 [cited 2024 Apr 17];14. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10679740/
Ash Sharma
Dr Ashwin Sharma is a medical doctor and writer with a particular interest in health technology, artificial intelligence and medical weight loss. He completed his training at the University of Leicester and Imperial College London, and has since been exploring the intersections of medicine, technology, and communication.