What does tranexamic acid do? Understanding skincare’s most underrated ingredient
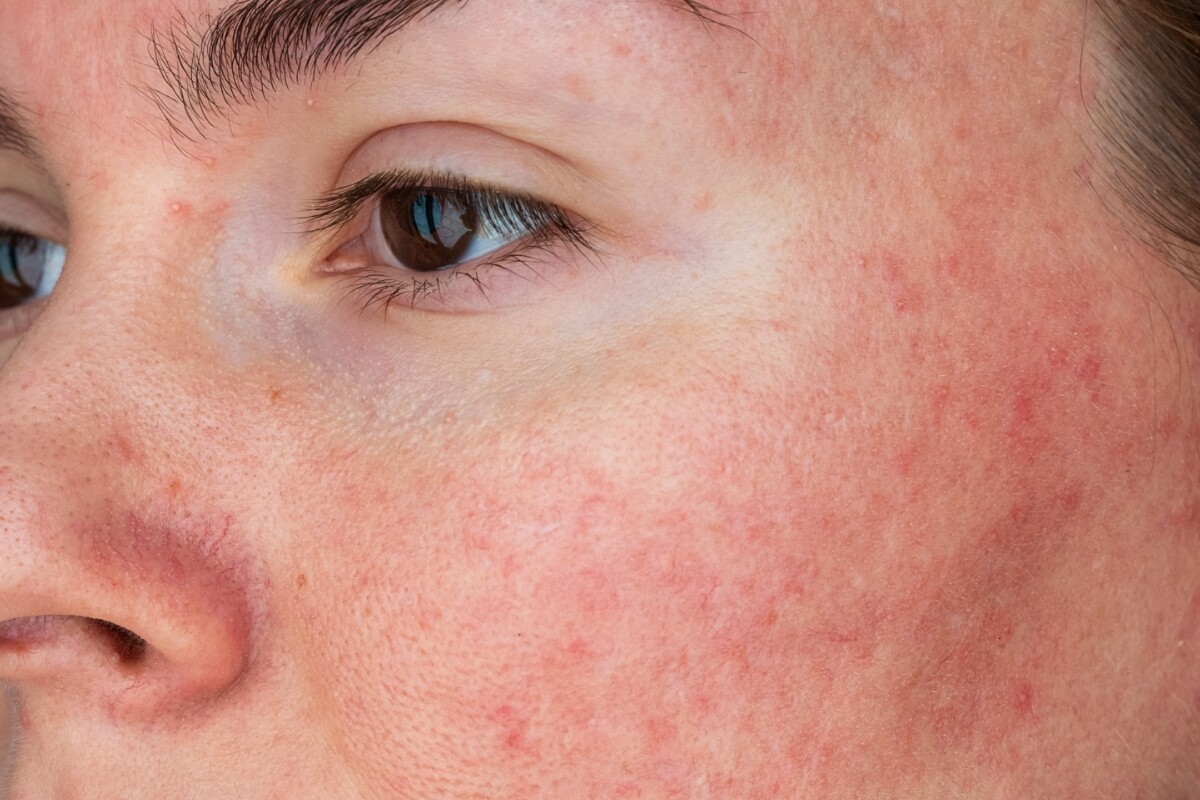
If you’re struggling with dark spots, melasma, dullness, or uneven skin tone, tranexamic acid could be the ingredient you’ve been searching for. Its multi-faceted approach to reducing pigmentation, combined with its gentle effects on the skin, has made it a game-changer in the world of skincare. In fact, it’s one of our dermatologists’ top ingredients for treating dark spots. With consistent use, you can look forward to brighter, clearer, and healthier-looking skin.
Here’s everything you need to know about what it is, how it works, how to use it, and what to expect in terms of results.
What is Tranexamic Acid (TXA)?
In topical skincare, Tranexamic acid, or TXA, is an over-the-counter ingredient that can help to fade discolouration and brighten the complexion. Studies have shown that it could be an effective treatment for melasma, dark spots and other pigmentation concerns such as post-acne marks.
Tranexamic acid also has anti-inflammatory properties, meaning it can benefit people with sensitive and reactive skin types, including people whose skin is prone to acne. Incorporating tranexamic acid into your regular skincare routine can help to brighten a dull complexion and promote more even, clearer-looking skin. [1]
How does Tranexamic Acid Work?
TXA comes from the amino acid lysine and has been used in a medical context to slow or prevent excessive bleeding. It works by reducing plasmin activity in the skin. Plasmin plays a role in inflammation and melanin production, so reducing it helps to reduce pigmentation. [2]
Because TXA helps to keep melanin production under control it can reduce the appearance of dark spots and prevent new ones from appearing [2]. TXA also reduces excessive blood flow, minimising redness and the appearance of blood vessels. High temperatures can also increase inflammation and blood flow within the skin, triggering or worsening hyperpigmentation in some people. TXA’s properties help to prevent this reaction.
Our Advanced Dark Spot Corrector Serum contains tranexamic acid along with glycolic acid and kojic acid, two complementary active ingredients that boost the overall effects.
What are the Benefits of Tranexamic Acid in Skincare?
In a 2021 study, subjects noticed their skin improved after using TXA, in as little as two weeks [3].
Depending on your skin type and the condition you’re looking to treat, results are generally visible from 6 weeks with consistent use.
You can use tranexamic acid to:
Reduce hyperpigmentation and dark spots
Even and brighten the complexion
Help lighten the appearance of melasma
Reduce the appearance of age spots, sun spots or liver spots
Minimise redness and inflammation
Reduce the risk of hyperpigmentation in acne-prone skin
Enhance overall skin tone and texture
Who can use Tranexamic Acid?
TXA is generally safe and effective for all skin types,including sensitive and rosacea-prone skin. It’s available over-the-counter, making it easier to access than prescription treatments. [4]
When treating melasma, dark spots or hyperpigmentation, hydroquinone is considered the gold-standard ingredient. When using hydroquinone, your dermatology expert will require you to take breaks during your treatment plan, as this powerful, highly effective active ingredient can be harsh on the skin.
Breaks aren’t necessary with tranexamic acid, meaning it’s a great option if you’re on a break from hydroquinone, or you’re not ready to commit to a hydroquinone prescription.
You can also combine tranexamic acid with retinoids like tretinoin, as neither ingredient requires downtime during your treatment plan.
How should I add Tranexamic Acid to my Skincare Routine?
Always introduce a new active ingredient to your skincare routine gradually. And unless you’ve been advised by a dermatologist, avoid using too many strong active ingredients together at the same time. It’s important to use the correct dosage of tranexamic acid to suit your skin, as too much can cause irritation — click here to find out more, or if you’re a subscriber you can speak with one of our dermatology experts through your Dermatica dashboard.
Watch out for these common pitfalls, and if you notice any irritation, stop using all actives and switch to a soothing, simple emollient moisturiser to help your skin recover. Once your skin has settled, you can reintroduce actives gradually and one at a time.
Can I use Tranexamic Acid with Other Active Ingredients?
Tranexamic acid is generally safe to use with other active ingredients, including:
AHAs (like glycolic acid, lactic acid or mandelic acid) and BHAs (like salicylic acid)
Retinoids, retinol or retinaldehyde
Hydroquinone
Vitamin C, including ascorbic acid
Niacinamide
Kojic acid
Ferulic acid
Relationship between Tranexamic acid, Dark Spots and Sun Damage
One of the leading causes of dark spots, melasma and hyperpigmentation is sun damage. Everyone should use broad-spectrum sunscreen every day, but this step is especially important when using actives like TXA, because active ingredients can make your skin more sensitive to UV rays.
Tip: Always use a sunscreen with at least SPF30+ to protect your skin, even on a cloudy day. Our SPF50 Photodamage Defence Sunscreen is ideal, because it offers protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
At Dermatica, our dermatology experts have successfully treated thousands of customers who wanted to reduce the appearance of dark spots, and most began to see results after just 8 weeks.
When you subscribe, our experts formulate a personalised treatment plan based on your pictures and your goals, taking the guesswork out of finding which formula will suit your skin. You’ll also gain unlimited access to our team – to ask questions about your skincare goals, ingredients like tranexamic acid, and your personalised formula.
Find out which Dermatica formulas are best suited to your skin by visiting our website.
References
1. Ebrahimi B, Naeini FF. Topical tranexamic acid as a promising treatment for melasma. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences : The Official Journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences [Internet]. 2014 Aug 1;19(8):753–7. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4235096/
atra J, Brar B, Kumar S, Arora H. Tranexamic acid in melasma: Comparative evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of oral tranexamic acid versus its transepidermal administration. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery. 2022;15(4):394.
2. da Silva Souza ID, Lampe L, Winn D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology [Internet]. 2021 Feb 1;20(2):561–5. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32588531/
3. Basit H, Godse KV, Al Aboud AM. Melasma [Internet]. PubMed. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459271/
Ash Sharma
Dr Ashwin Sharma is a medical doctor and writer with a particular interest in health technology, artificial intelligence and medical weight loss. He completed his training at the University of Leicester and Imperial College London, and has since been exploring the intersections of medicine, technology, and communication.